Introduction
The financial industry pioneered digital transformation, from the introduction of magnetic stripe cards in the 50s, ATMs in the 60s and electronic trading platforms in the 70s. The 2008 Great Recession catalysed a wave of new policies and practices driven by public demand for transparency. This era also ushered in the rise of “challenger banks” and digital-first financial institutions (fintechs) where technology is a core differentiator.
The COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 accelerated digital adoption, enabling remote services, enhanced customer experiences, and remote workforce management. Banks increased technology spending by 38% between 2013 and 2022, now 20% of their total expenses and approximately 17% of global IT spending.
Meanwhile, financial institutions operate under intense regulatory scrutiny, navigating frameworks such as AML (Anti-Money Laundering), GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), and KYC (Know Your Customer). Compliance has grown increasingly complex, with costs skyrocketing. Large institutions spend over $10,000 per employee annually on compliance, often exceeding $200 million for banks with over 20,000 employees. These processes are labour-intensive, error-prone, and risky.
Platforms like Microsoft’s Copilot and Power Platform offer prebuilt solutions, while custom-built systems leveraging small language models (SLMs) provide bespoke alternatives. Both approaches hold immense potential for automating compliance, simplifying workflows, and minimising risks.
Navigating Compliance in Finance
Evolving Complexity
Financial institutions must navigate a labyrinth of ever-changing regulations such as CRR (Capital Requirements Regulation), BRRD (Bank Recovery and Resolution Directive), PSD2 (Revised Payment Services Directive), GDPR, and AML. Adapting to these changes can strain resources and lead to delays.
Rising Costs of Compliance Operations
Manual audits and transaction monitoring are resource-intensive and drive up compliance costs. The inefficiencies inherent in these traditional approaches often result in significant financial and operational burdens. Global financial crime compliance costs reached $181 billion back in 2021 and $206 billion in 2023.
Human Error Risks in Compliance Processes
Traditional compliance systems operate reactively, leaving organisations vulnerable to undetected risks. Real-time monitoring and reporting remain critical gaps in many financial institutions.
How AI Agents Address Compliance Challenges
Agentic compliance leverages AI systems to automate and optimise compliance processes. The synergy between AI (e.g., Copilot) and low-code technologies (e.g., Microsoft’s Power Platform) allows users to create sophisticated solutions quickly and efficiently, regardless of their coding expertise. Organisations can build and deploy multi-agent workflows that simplify tasks:
- KYC and Due Diligence: Generative AI agents extract and interpret text-based data, handling specifics that previously relied on human expertise.
- Transaction Monitoring: AI agents proactively detect anomalies, trigger preemptive actions, and escalate suspicious activities to specialised teams, ensuring continuous monitoring.
- AI-Enhanced Governance and Oversight: AI agents monitor communications, detect breaches of policies, and provide guidance on regulatory compliance.
- Regulatory Reporting: AI automates the generation of compliance reports, flagging anomalies, and triggering workflows to meet reporting timelines accurately.
Custom solutions using tools like LlamaIndex and SLMs (Small Language Models) allow businesses to tailor workflows to specific needs. These solutions integrate seamlessly into existing tech stacks using frameworks such as LangChain.
Comparing Microsoft-Based Solutions vs. Custom Solutions
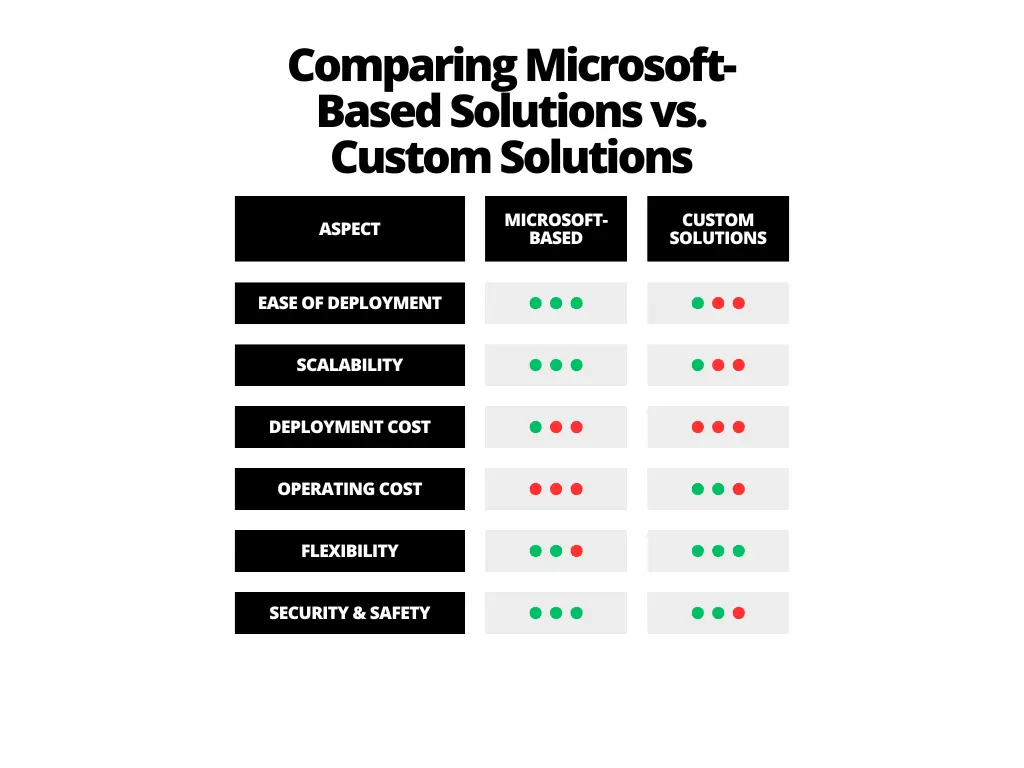
Table 1: Key Differences: Microsoft-Based Solutions vs. Custom Solutions (Diev, 2024)
Real-World Applications of Agentic Compliance
Audit and Regulatory Reporting: AI aggregates data to generate comprehensive audit reports, ensuring consistency and minimising manual interventions.
Streamlined KYC and Onboarding: Generative AI agents verify identities, identify discrepancies, and enhance KYC compliance while reducing manual oversight.
AI Transaction Monitoring: AI agents powered by Microsoft’s Azure OpenAI Service proactively detect anomalies, notify stakeholders, and launch investigations.
Data Privacy and Governance: AI agents monitor access to sensitive data, ensuring compliance with GDPR and AML directives.
Visual Framework for Agentic Compliance
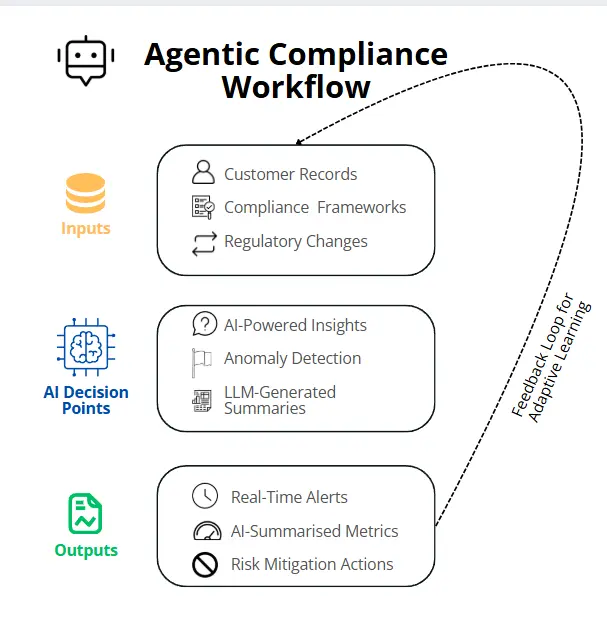
Figure 1 illustrates how agentic compliance integrates data inputs, AI decision points, and actionable outputs into a streamlined regulatory framework (Diev, 2024).
Potential ROI effects
- Labour Cost Reduction: Labour accounts for approximately 60% of compliance costs in large financial institutions.
- Error Mitigation Savings: AI can reduce manual errors, leading to fewer regulatory fines and operational inefficiencies, saving millions in some cases.
- Efficiency Gains: Automating compliance reporting and enhancing real-time monitoring can save $10M by minimising delays and streamlining operations. Actual results may vary based on the institution’s existing systems and regulatory complexity.
Conclusion
Agentic compliance offers unparalleled advantages for financial institutions by addressing some of the most pressing challenges in regulatory adherence. Key benefits include:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Immediate detection and reporting of compliance breaches, reducing risk exposure.
- Cost Efficiency: Automated compliance tasks significantly reduce operational costs.
- Scalability: AI systems adapt seamlessly to increased transaction volumes and evolving regulations.
- Enhanced Accuracy: Minimising human error ensures more reliable compliance processes.
While the benefits are substantial, institutions must also navigate challenges such as initial implementation costs, staff training, and ensuring data privacy compliance. Microsoft’s Copilot and Power Platform provide powerful, easy-to-deploy solutions for standardised tasks, whereas custom-built systems offer the flexibility needed for specialised workflows. These use cases are already delivering returns on investment of several hundred per cent, showcasing the transformative potential of AI-driven compliance solutions.


