Super Apps (or “everything apps”) offer multiple services in one place. You can connect, shop, pay, bank, or invest within them. But in 2025, AI agent interfaces are emerging that can autonomously crawl and act on users’ behalf, blurring the lines between single-purpose apps and multi-service super apps.
This shift presents a game-changing opportunity for banks and retailers—especially in the US and EU, where super apps have traditionally lagged behind their Asian counterparts. True super apps (such as China’s WeChat) have been rare and region-specific. However, API-accessible AI agents now have the potential to democratise this model globally. Finance-led and commerce-led apps—from Revolut to Amazon—are actively exploring how to embed these autonomous agents into their ecosystems.
Take Amazon’s Buy for Me feature. It goes beyond Amazon’s typical marketplace model by crawling third-party platforms and completing purchases on behalf of the customer. In essence, Amazon’s shopping app is beginning to behave like a super app—enabling users to complete nearly any task that’s accessible on the web, all from one interface.
Comparing Key Players
Companies across tech and finance are converging on AI agents as the key to offering super app-like experiences. Each is taking a different route based on their strengths – e-commerce giants extend shopping beyond their walls, fintechs leverage AI to boost financial services, and AI platform providers enable any app to become “super.” Below is a short comparison table:
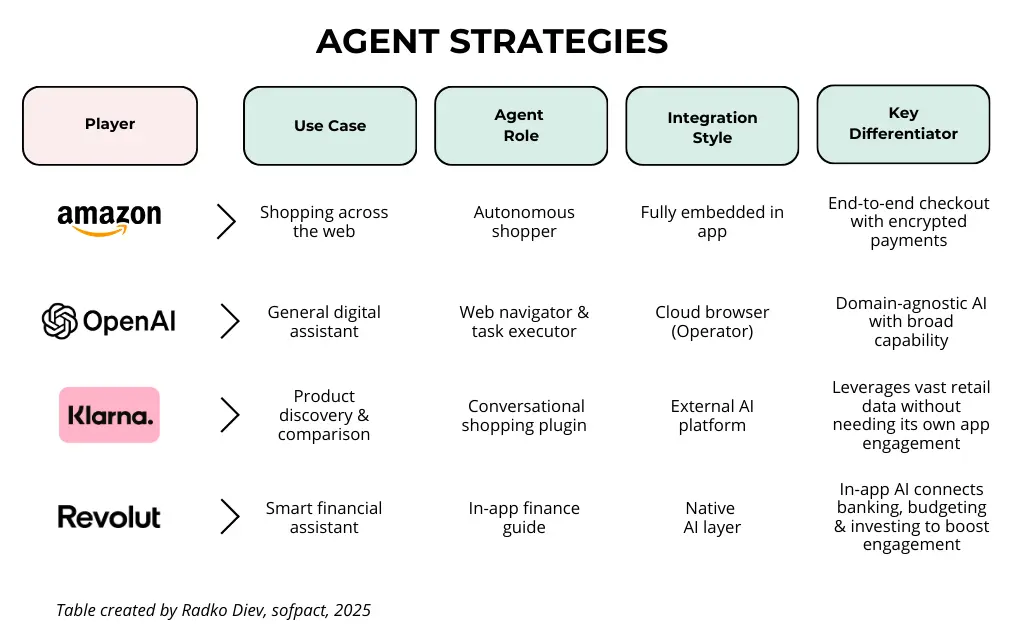
Amazon and Revolut are building tightly integrated, in-house AI agents to deepen control over their ecosystems, while OpenAI and Klarna are enabling plug-and-play intelligence across other platforms. Amazon focuses on expanding its shopping reach while keeping trust and payments in-house. Revolut uses AI to simplify and personalise its complex service suite. In contrast, Klarna extends its commerce engine into external AI (like ChatGPT), and OpenAI offers a universal AI layer that works across domains—without owning any commerce or finance stack.
Toward an Agent-Powered App Ecosystem
With generative AI and agentic interfaces, Western firms no longer need to replicate the WeChat model of creating an empire of mini-apps. Instead, AI agents act as universal adapters, connecting apps to external services on demand.
One crucial advantage of this model is overcoming consumer reluctance around trusting a single app with extensive personal data. Because the AI agent works transparently and securely on users’ behalf—handling tasks across multiple providers without centralising their data—consumers retain greater control. Amazon’s “Buy for Me” feature is a prime example: it processes external transactions securely without accessing order details, increasing user trust.
Historically, the competitive landscape also presented barriers. Previously, companies had to either acquire or build numerous services internally to achieve super-app status. Today, partnerships suffice. Banks and retailers can collaborate easily with fintech, travel, and retail platforms through API-accessible AI agents. According to McKinsey, generative AI significantly improves customer service efficiency, enabling businesses to extend beyond their traditional boundaries without major acquisitions or complex integrations. Even dominant Asian super apps like WeChat are embracing AI-driven innovation to maintain their competitive edge.
Companies adopting this approach will choose between developing proprietary in-app agents or integrating third-party AI assistants. Amazon and Revolut, for example, maintain tight control with proprietary solutions, while Klarna and OpenAI offer more flexible integrations into external apps (See the AI Agent Strategies infographic by Radko Diev, sofpact 2025).
Looking ahead, this shift is set to dramatically reshape digital commerce. According to ARK Invest, AI shopping agents could power up to $9 trillion in online spending annually by 2030, accounting for nearly a quarter of global e-commerce. Digital wallets with embedded AI capabilities could manage up to 72% of these transactions, underscoring how transformative this trend might become.
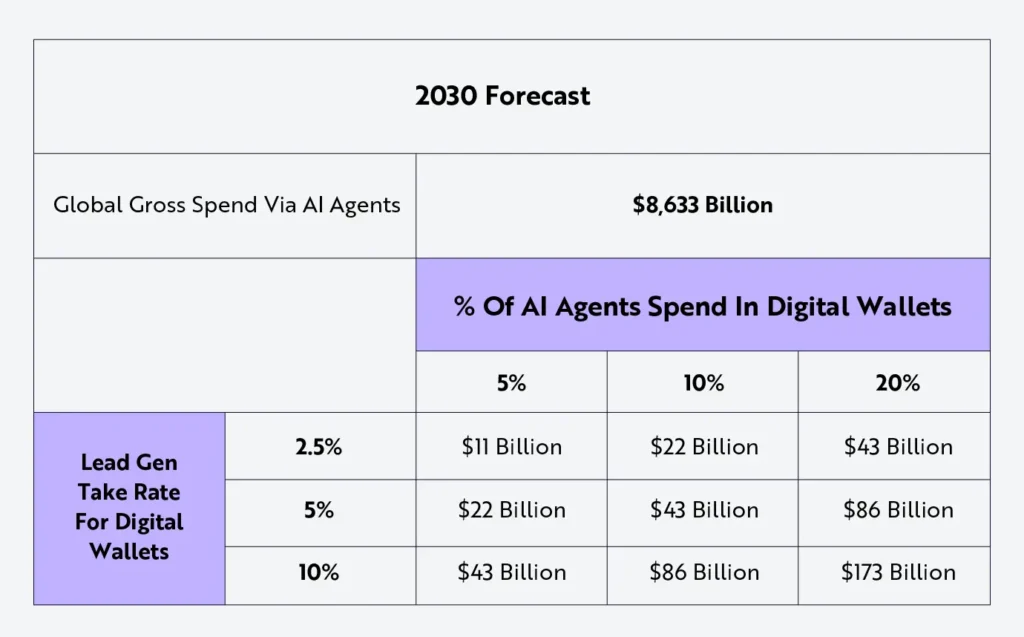
Source: ARK Investment Management LLC, October 2024. Used for educational and commentary purposes.
2025 marks a tipping point—where technology maturity aligns with rising consumer expectations. Businesses embracing AI agents today are poised to lead the next wave of digital transformation, offering seamless, hyper-personalised experiences without needing to control every service category.
The Western “super app” may not be a single, all-in-one platform—but rather an intelligent layer that connects best-in-class apps into one cohesive user journey. Instead of building monopolies, forward-thinking companies can now integrate, partner, and let AI do the heavy lifting—unlocking loyalty and growth through smart orchestration.
Whether managing finances, shopping, or travel, consumers will increasingly rely on AI assistants acting on their behalf. This emerging ecosystem promises a richer digital life—and creates significant strategic opportunities for banks, retailers, and digital platforms ready to lead.
Executive Takeaways
- AI agents are reshaping digital strategy, turning single-purpose apps into intelligent, multi-capability platforms.
- Super app potential is now democratised, enabled by open APIs and modular AI—not just reserved for tech giants.
- Agent-first design drives retention and value, especially in fintech, ecommerce, banking, and consumer services.



